Feasible solutions
Advanced endoscopy
We offer several minimally invasive techniques to treat health conditions that previously required conventional surgical interventions with higher risks and much longer recovery periods.
01.
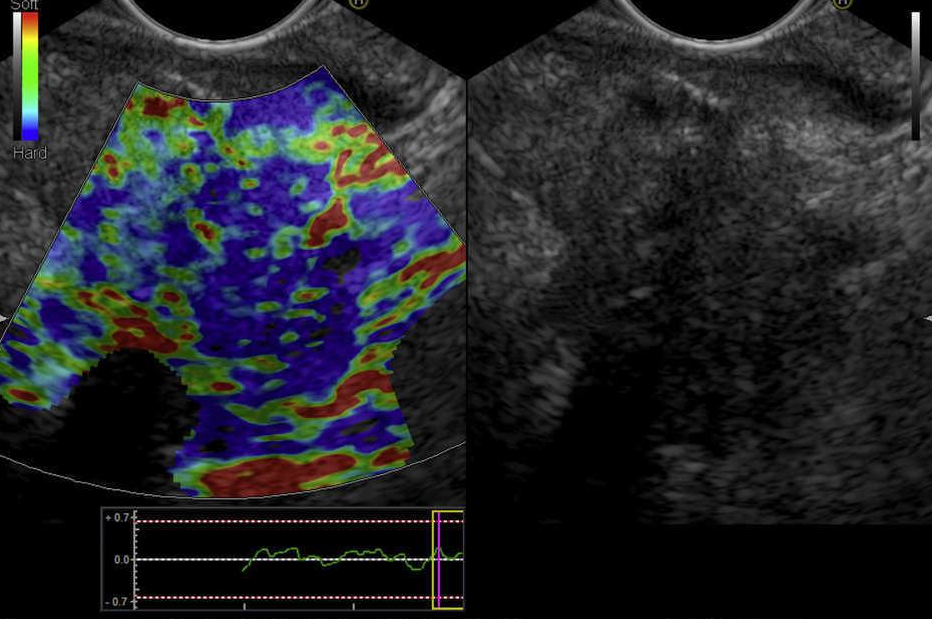
Endoscopic ultrasound
Endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) or echoendoscopy is a technique that combines gastroscopy with ultrasound by using ultrasound to reproduce images of the internal structures of the digestive system or close to it, with very high sensitivity, even higher in some cases when compared with magnetic resonance or tomography.
The technique makes it possible to study tumor lesions, determining their characteristics, location and depth. It also allows obtaining samples or biopsies of lesions by means of fine needle aspiration and puncture (PAAF). This variant is known as USE-PAAF.
The EUS helps and provides more information than other imaging tests, allowing for the most accurate diagnosis of digestive pathologies and lesions in the bile ducts.
The main applications are:
– Evaluation and staging of subepithelial tumors in the esophagus, stomach, duodenum or rectum.
– Identify stones or microlithiasis in dilated bile ducts not observed by resonance or tomography.
– Drainage of pseudocysts and bile duct lesions.
– Drainage of pancreatic, liver or rectal abscesses
– Evaluation of recurrent pancreatitis or without identified cause
– Diagnosis of cystic tumors of the pancreas.
Fine needle puncture of tumors in the esophagus, stomach, pancreas, liver and bile ducts.
– Evaluation of rectal and anal lesions: abscesses, fistulas, tumors.
– Evaluation and staging of gastric tumors (gastrointestinal lymphoma, gastrointestinal submucosal lesions, gastric cancer)
– Evaluation in chronic pancreatitis.
– Diagnosis and staging of ampullary tumors.

02.
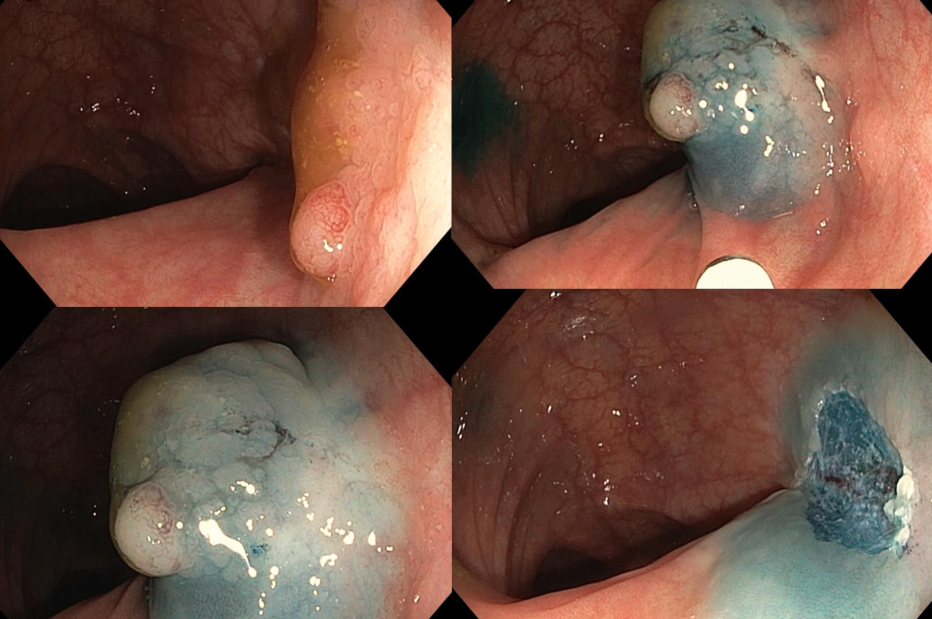
Mucosectomy
Endoscopic mucosectomy or mucosal resection is a technique for dissecting precancerous lesions and superficial cancer of the digestive tract.
70-80% of digestive tract cancers originate from an adenomatous polyp that undergoes a malignant transformation process to become an adenocarcinoma (cancer). These tumors can be detected and treated endoscopically by means of mucosectomy, when they are in the form of polyps, prior to their malignancy.
The procedure is a less invasive alternative to surgery to remove advanced lesions, especially large polyps that develop in the digestive tract.
Mucosectomy has proven to be an effective option in expert hands with experience in the technique for the treatment of early-stage superficial cancer and precancerous lesions that can evolve into malignancy.
03.
Enteroscopy
Double balloon enteroscopy is an endoscopic technique that helps us diagnose and treat diseases of the midgut (jejunum, ileum, and distal part of the duodenum) where conventional gastroscopy or colonoscopy cannot be reached.
The main indications indications:
– Gastrointestinal bleeding of unknown origin, that is, in which it has not been possible to find a cause despite having studied it with conventional endoscopies.
– Anemia study
– Findings of an irregular area in the midgut seen by resonance or tomography.
– Suspected inflammatory bowel diseases (for example Crohn’s disease).
– Suspected tumor
– Familial polyps and polyposis (such as Peutz-Jeghers syndrome).
– Study of chronic diarrhea or unexplained malabsorption syndrome.

04.
(ERCP)
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a technique that combines endoscopy (duodenoscopy) and X-rays to study the drainage tubes of the gallbladder, pancreas, and liver (called bile ducts).
Main indications are:
– Removal of gallstones trapped in the bile duct (choledocholitis)
– Infection (Cholangitis)
– Acute pancreatitis due to lithiasis
– Tumors or cancers in the bile ducts
– Tumors or cancers of the pancreas
– Chronic pancreatitis
– Trauma or surgical complications to the bile or pancreatic ducts

05.
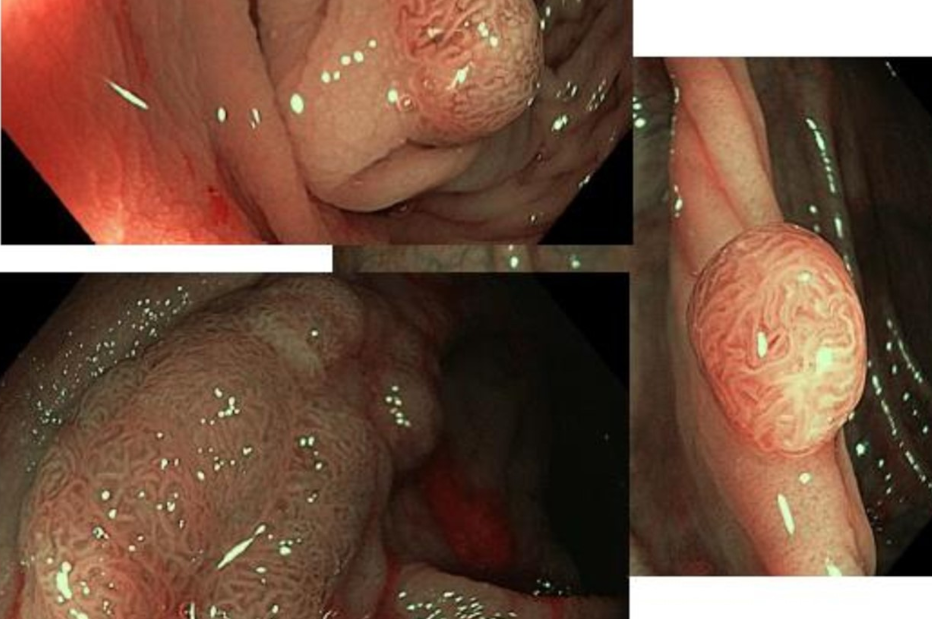
Early detection of injuries
In the last decade, considerable progress has been achieved in modern advanced endoscopic imaging techniques, acquiring a great impact in the detection and characterization of precancerous and cancerous lesions of the intestine that, in the eyes of trained endoscopists, give the possibility of their early histopathological diagnosis.
Early detection of lesions is supported by high-definition endoscopy and with or without optical magnification, enhanced with contrast or computerized filters (digital chromoendoscopy) to help achieve a higher percentage of early detection, compared to conventional white light endoscopy.
Potential indications:
– Assessment of hyperplastic and adenomatous polyps
– Diagnosis and follow-up in Barrett’s esophagus
– Evaluation and monitoring of premalignant lesions
– Analysis of atypia or superficial cancer
-Early diagnosis of injuries
– Assessment in gastroesophageal reflux disease
– Evaluation of gastric metaplasia
– Assessment of atrophy (celiac disease)
– Diagnosis and monitoring of inflammatory bowel disease
06.
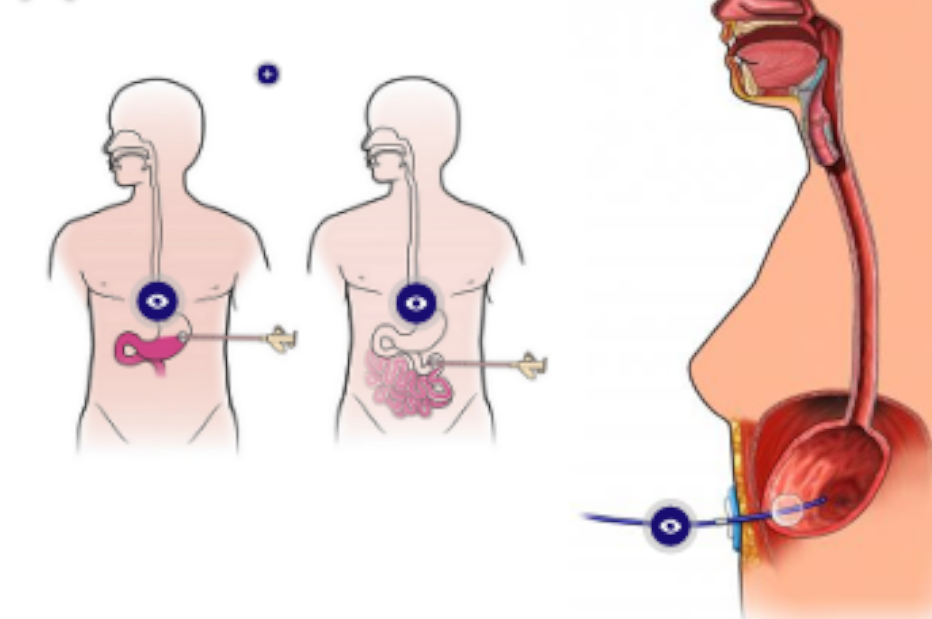
Endoscopic gastrostomy and jejunostomy
This technique involves placing a soft, rubber tube through the skin of the abdomen into the stomach (gastrostomy/PEG) or into the part of the small intestine called the jejunum (jejunostomy).
Through the tube, it is possible to feed and administer medications until the person is in adequate and healthy conditions to be fed by mouth.
The main indication for these procedures is to maintain enteral nutrition in patients with an intact digestive system but with reversible or irreversible swallowing disorders, obstruction or other causes that make it impossible to continue said nutrition by the oral route.
07.
Advanced Gastroscopy and Colonoscopy
Advanced gastroscopy and colonoscopy is the improved practice in experienced hands of conventional endoscopy that will cover a broad spectrum of newer interventional and complex techniques.
We use state-of-the-art technologies such as virtual chromoendoscopy, magnification, high definition images and the default application in the required cases of early optical diagnosis, polypectomies and complex mucosectomies, avoiding deferring the patient for later application in a second act.
08.
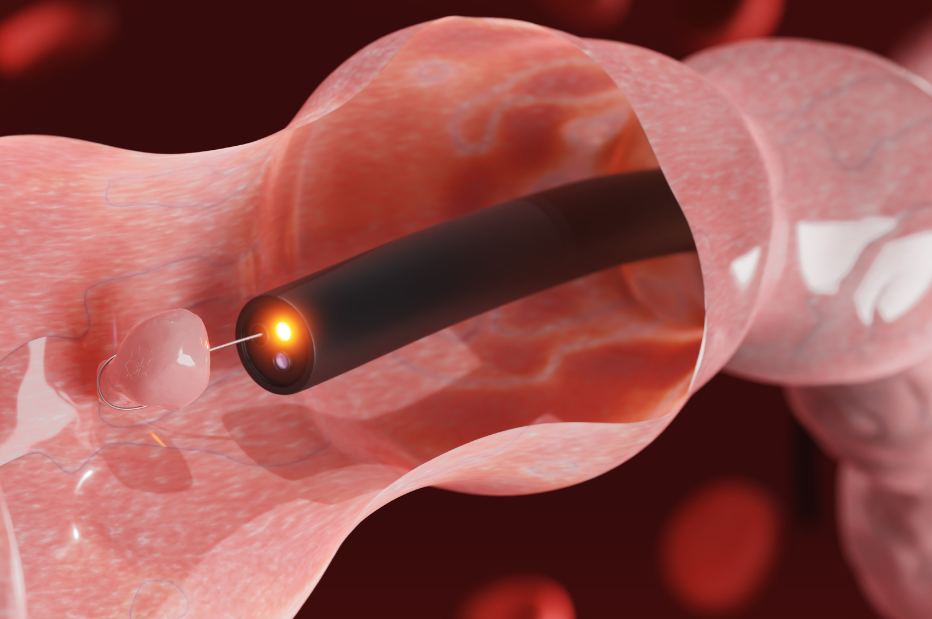
Complex Polypectomy
It is an outpatient procedure that consists of resecting or endoscopically removing flat or elevated polyps that present a challenging location and diameter and that require advanced resection techniques.
09.
Endoscopic dilations
Endoscopic dilation is a procedure that widens or enlarges a stenosis or narrowing in an area of the digestive tract.
The technique makes it possible to treat a series of pathologies in which the alternative is surgical treatment, and its objective is to achieve a sufficiently large increase in the caliber of the organ’s lumen, to improve symptoms.
Applications can be:
Benign stenosis in:
– Esophagus
– Cardia
– Stomach
– pylorus
– Duodenum
– ileum
– colon
– Achalasia
– Peptide stenosis
– Schatzki ring
– Reflux stricture
– Post-bariatric surgery stenosis
